Present Perfect Tense
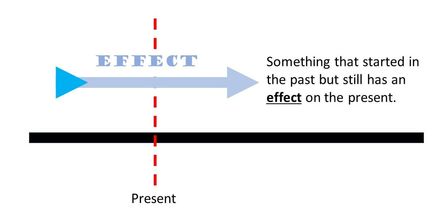
The present prefect tense is used to talk about an activity or event that happened in the past but still has an effect on the present.
Form:
Has + past participle
Have + past participle
Note the use of Present Prefect Tense with a fixed time expression.
The present prefect tense is used to talk about an activity or event that happened in the past but still has an effect on the present.
Form:
Has + past participle
Have + past participle
- I have lost my favourite story book.
- Who has taken the painting?
- Johnny has taken his dinner.
Note the use of Present Prefect Tense with a fixed time expression.
- Jane has gone to Australia. (correct)
- Jane has gone to Australia last month* (incorrect)
- Jane has been living in Australia since 2005 (correct)
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
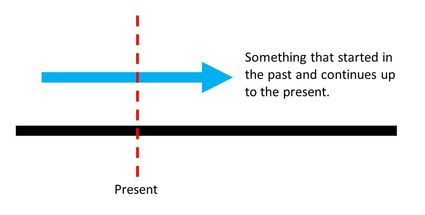
The present prefect continue tense is used to talk about things that started in the past and continues up to the present.
Form:
Have + been + present participle
Has + been + present participle
The present prefect continue tense is used to talk about things that started in the past and continues up to the present.
Form:
Have + been + present participle
Has + been + present participle
- My sister has been talking on the phone for the past one hour. (She is still talking on the phone.)
- The fans have been waiting at the airport for their favourite actor since this morning. (They are still waiting for him.)
- Have you been practising piano lately?
- Benny has been hiding in his room since yesterday.
Past Perfect Tense
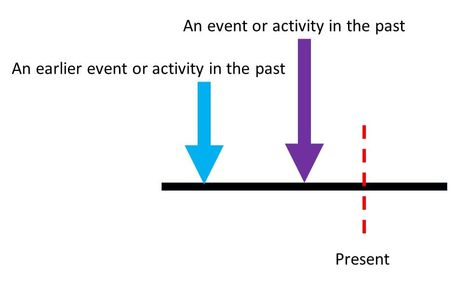
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe two events that happened in the past. It shows the end of one event before another event happened. Some people also refers to this as ‘the past of the past’.
Form:
had + past participle
The Past Perfect Tense is used to describe two events that happened in the past. It shows the end of one event before another event happened. Some people also refers to this as ‘the past of the past’.
Form:
had + past participle
- I noticed that he had left his mobile phone behind.
- The author had written only one book when he became famous.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
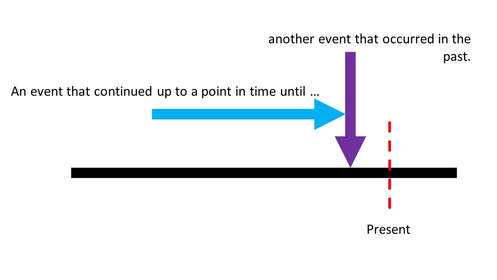
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is used to talk about an event that continued up to a point in time in the past. It is used to describe a thing that was going on in the past before something else occurred.
Form:
had + been + present participle
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is used to talk about an event that continued up to a point in time in the past. It is used to describe a thing that was going on in the past before something else occurred.
Form:
had + been + present participle
- Jack had been wondering what to eat for dinner when his neighbour brought him a box of pizza.
- Timothy had been repairing his computer for the past two days, but he eventually gave up.
- The children had been running around in class until the teacher walked in.
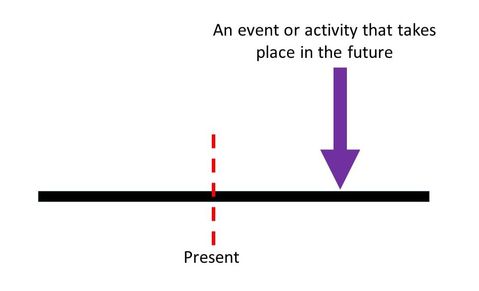
Simple Future Tense
The Future Tense is used to describe an event that takes place in the future. The form of the verb does not change, instead, the Future Tense is expressed by using helping verbs like will and shall.
Form:
modal + base form of verb
The Future Tense is used to describe an event that takes place in the future. The form of the verb does not change, instead, the Future Tense is expressed by using helping verbs like will and shall.
Form:
modal + base form of verb
- She will leave in five minutes.
- Shall we meet for lunch tomorrow?
- Mr Tan will send his car to the workshop later this afternoon.
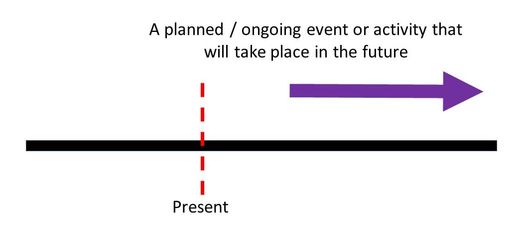
Future Continuous Tense
The Future Continuous Tense is used to describe an event that has be planned or an ongoing action that will take place in the future.
Form:
Shall + be + present participle
Will + be + present participle
The Future Continuous Tense is used to describe an event that has be planned or an ongoing action that will take place in the future.
Form:
Shall + be + present participle
Will + be + present participle
- Mrs Tay will be waiting at the entrance to pick up her daughter after her dance lesson.
- We will be celebrating Mum’s birthday at a chalet tomorrow.
- Will you be attending Jane’s wedding this weekend?
- Later this evening, I shall be painting in my room.
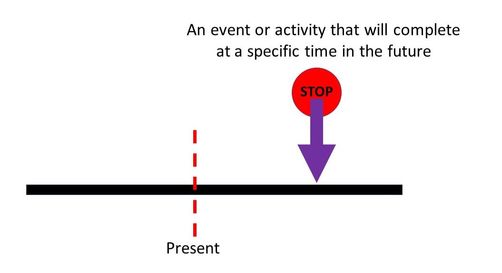
Future Perfect Tense
The Future Perfect Tense is used to talk about an event that will have ended at a particular time in the future.
Form:
will + have + past participle
The Future Perfect Tense is used to talk about an event that will have ended at a particular time in the future.
Form:
will + have + past participle
- I will have completed the assignment by the time you arrive.
- Patrick will have spent all his allowance by the end of this week.
- The train will have left the station when you reach there.